What are 20 warning signs of cancer?
What are 20 warning signs of cancer? Cancer warning signs can vary widely depending on the type of cancer, but there are several common symptoms that may indicate a potential issue.
If you experience any of these warning signs, especially if they persist or worsen, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation. Early detection is key to successful treatment and can significantly improve outcomes.
20 warning signs of cancer
Cancer symptoms vary by type and can be subtle, but here are 20 general warning signs that could suggest cancer and warrant medical attention:
1. Unexplained weight loss – losing 10 pounds or more without trying can be an early sign, particularly for cancers of the pancreas, stomach, esophagus, or lung.
2. Persistent fatigue – feeling extremely tired without relief from rest might signal leukemia, colon, or stomach cancer.
3. Persistent pain – unexplained pain that doesn’t improve could point to various cancers, including bone or testicular cancer.
4. Lump or swelling – new lumps, especially in the breast, testicles, neck, or armpits, can indicate cancer.
5. Changes in skin – darkening, yellowing, redness, sores that don’t heal, or mole changes could suggest skin cancer.
6. Persistent cough or hoarseness – a long-lasting cough, hoarseness, or breathing changes can be a symptom of lung or throat cancer.
7. Difficulty swallowing – having trouble swallowing may signal throat or esophageal cancer.
8. Unusual bleeding or bruising – blood in the urine or stool, unusual vaginal bleeding, or unexpected bruising may indicate cancers like colon or bladder cancer.
9. Changes in bowel habits – long-term constipation, diarrhea, or changes in stool shape may signal colon cancer.
10. Persistent bloating or abdominal pain – can be a sign of ovarian, pancreatic, or stomach cancer.
11. Frequent infections – frequent infections, fevers, or chills can be early signs of blood cancers like leukemia.
12. Difficulty urinating – pain, discomfort, or difficulty urinating can signal prostate cancer.
13. Sores that don’t heal – particularly in the mouth or on the skin, could be signs of oral cancer or skin cancer.
14. Unusual discharge – persistent, unusual discharge from any part of the body can be a red flag.
15. Nausea or vomiting – persistent nausea or vomiting could be a symptom of cancers affecting the digestive tract.
16. Night sweats – unexplained, excessive night sweats can sometimes point to lymphoma.
17. Persistent indigestion – can be a symptom of cancers affecting the stomach or throat.
18. Mouth sores or white patches – especially on the gums, tongue, or inside the mouth, could signal oral cancer.
19. Swelling in the face or neck – particularly swelling that isn’t explained by allergies or infections can be concerning.
20. Persistent muscle or joint pain – unexplained aches that don’t improve may indicate bone or soft tissue cancers.
These symptoms are not exclusive to cancer and can often be due to other, less serious conditions. However, if they persist or worsen, it’s wise to consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation.
Cancer warning signs
We have discussed here 20 warning signs of cancer. You can get a detailed idea about the 10 symptoms from the following article. We have also discussed the 20 symptoms in the above section. Hope you can easily understand.
1. Unexplained weight loss
Unexplained weight loss, especially when it happens rapidly or without intentional lifestyle changes like diet or exercise, is often considered an important warning sign for various health conditions, including cancer. Losing 10 pounds or more without a clear reason can sometimes point to cancers affecting the:
- Digestive system: Cancers of the stomach, esophagus, pancreas, or colon can interfere with normal digestion and lead to unexpected weight loss.
- Lungs: Lung cancer may cause weight loss due to loss of appetite or other metabolic changes.
- Blood and lymph: Cancers like leukemia and lymphoma can also lead to significant weight loss due to high energy use from immune responses and rapid cell turnover.
Cancer cells tend to use up a lot of energy and nutrients, and in many cases, they disrupt the body’s metabolism. Cancer can also affect hormone levels and immune function, leading to increased calorie consumption or reduced nutrient absorption.
Weight loss may be one of the earliest noticeable symptoms, and it should be evaluated, especially if it’s paired with other signs like fatigue, digestive issues, or changes in appetite.
2. Persistent fatigue
Persistent fatigue is a common symptom in many types of cancer and can feel different from normal tiredness. This fatigue often doesn’t go away with rest and can significantly impact daily activities, concentration, and quality of life. In cancer, fatigue can result from several causes:
- Metabolic changes: Cancer cells can alter the body’s metabolism, causing an increase in energy expenditure and contributing to exhaustion.
- Anemia: Certain cancers, particularly blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma, can lead to a reduction in red blood cells, causing anemia and reducing oxygen transport, which leads to fatigue.
- Immune response: As the body fights the cancer, the immune system releases chemicals (cytokines) that can induce fatigue.
- Cancer treatments: Radiation, chemotherapy, and other cancer treatments often cause prolonged fatigue as a side effect.
Persistent fatigue that doesn’t improve with adequate sleep, rest, or nutrition, and is associated with other symptoms (like weight loss, fever, or pain), should be evaluated by a healthcare provider. Fatigue on its own isn’t specific to cancer, but if it’s unexplained and long-lasting, it’s worth investigating.
3. Persistent pain
Persistent pain that doesn’t have an obvious cause and doesn’t improve with usual treatments can sometimes be a warning sign of cancer. While not all persistent pain is due to cancer, unexplained pain, especially if it’s severe or worsening, may signal an underlying issue, depending on its location and type:
- Bone pain: Could be a sign of bone cancer or cancers that have spread to the bones (such as breast, prostate, or lung cancer).
- Headaches: Chronic headaches, especially when paired with other neurological symptoms (like vision changes or coordination issues), could indicate a brain tumor.
- Back or abdominal pain: Persistent pain in the abdomen or back may suggest cancers of the pancreas, kidneys, or reproductive organs.
- Chest pain: Ongoing chest pain or discomfort might be associated with lung cancer.
Cancer-related pain can have several causes, including pressure on nearby nerves or organs, inflammation, or bone weakening. It can feel dull, sharp, or aching and may come on gradually.
If pain is unresponsive to usual treatments and persists without clear cause, it’s important to have it evaluated, especially if it’s accompanied by other symptoms like weight loss, fatigue, or changes in appetite.
4. Lump or swelling
The presence of a lump or swelling in any part of the body can be a concerning symptom and may indicate a range of health issues, including cancer. While many lumps and swellings are benign (non-cancerous), it’s important to pay attention to the following factors:
Common Types of Lumps and Their Implications:
Breast lumps: Changes in breast tissue, including lumps, could signal breast cancer. Regular self-exams and mammograms are important for early detection.
Lumps in the neck or armpits: Swollen lymph nodes in these areas can indicate lymphoma or other cancers, especially if they are hard, painless, and persist over time.
Testicular lumps: A lump in the testicle may be a sign of testicular cancer, especially if accompanied by pain or swelling.
Abdominal lumps: Swelling or lumps in the abdomen could indicate tumors in organs such as the liver, kidneys, or ovaries.
Soft tissue lumps: Lumps in soft tissues (muscles, fat, or connective tissue) can be benign, but certain types, like sarcomas, may indicate cancer.
Characteristics to Monitor:
- Size and shape: Lumps that grow or change shape over time should be evaluated.
Pain: Painless lumps are more concerning, but painful lumps can also indicate malignancy. - Consistency: Hard, immovable lumps are more suspicious than soft, movable ones.
- Duration: Lumps that do not go away or continue to grow should prompt further investigation.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
If you discover a lump or swelling that persists for more than a couple of weeks, changes in size or shape, or is associated with other symptoms (such as unexplained weight loss, night sweats, or persistent fatigue, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment, especially in cancer cases.
5. Changes in skin
Changes in the skin can be significant warning signs of cancer, particularly skin cancer, but they can also indicate other types of cancers. Here are some key changes to watch for:
Types of Skin Changes to Monitor:
Moles or growths: New moles or changes in existing moles (color, size, shape) can signal melanoma, the most serious form of skin cancer. The ABCDE rule is often used to assess moles:
- Asymmetry: One half is different from the other.
- Border: Irregular, jagged, or blurred edges.
- Color: Varied colors within the mole (brown, black, tan, red, white, or blue).
- Diameter: Larger than 6 mm (about the size of a pencil eraser).
- Evolving: Changes in size, shape, or color over time.
Redness or yellowing of the skin: Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) may indicate liver cancer or other liver diseases, while redness could suggest inflammatory conditions or lymphoma.
Unexplained sores or wounds: Sores that do not heal or persistent skin lesions can be indicative of skin cancer or other malignancies.
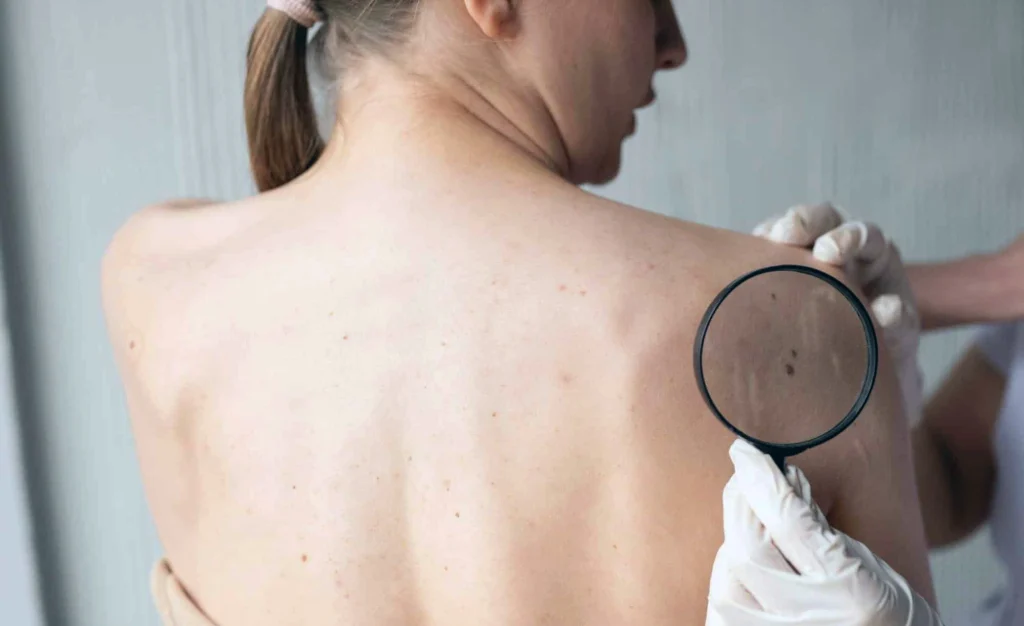
Rashes: New rashes, particularly those that are itchy or do not respond to treatment, should be examined, as they may be linked to conditions like cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
Lumps under the skin: Hard or painful lumps that appear under the skin can suggest skin cancer or other types of cancer, such as sarcoma.
Changes in texture: Areas of the skin that become rough, scaly, or develop patches may indicate actinic keratosis, which can be a precursor to skin cancer.
Other Signs Associated with Skin Changes:
- Excessive dryness or flakiness: Persistent dry skin that doesn’t improve could be linked to underlying health issues.
- Unexplained bruising: Easy bruising or skin that is unusually sensitive may indicate blood disorders associated with certain cancers.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
If you notice any of these changes, particularly if they persist or are accompanied by other symptoms (such as unexplained weight loss, fatigue, or lumps), it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. Early detection of skin changes can lead to timely intervention, especially for skin cancer and other related conditions.
6. Persistent cough or hoarseness
A persistent cough or hoarseness can be significant warning signs, especially if they last more than a few weeks and are not attributed to a known condition such as a cold or allergies. These symptoms can indicate various health issues, including cancer, particularly in the respiratory system. Here are some key points to consider:
Causes of Persistent Cough or Hoarseness:
Lung Cancer: A persistent cough, especially if it worsens over time, may be one of the first signs of lung cancer. It can be accompanied by other symptoms such as coughing up blood, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
Throat Cancer: Hoarseness or changes in the voice that last for more than a few weeks can indicate throat cancer (laryngeal cancer). This may also be associated with a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, or a lump in the throat.
Laryngeal Cancer: Cancer of the voice box can lead to persistent hoarseness, often without any other obvious cause. It may also affect the ability to speak normally.
Esophageal Cancer: Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), along with a persistent cough, can sometimes indicate esophageal cancer, especially if accompanied by weight loss or heartburn.
Head and Neck Cancers: Cancers in the head or neck area can also cause changes in the voice and persistent cough, often due to the location’s effect on nearby structures.
Other Associated Symptoms:
- Coughing up blood: This is a serious symptom that should prompt immediate medical evaluation.
- Sore throat or pain: A persistent sore throat, especially when coupled with hoarseness, may indicate an underlying issue.
- Difficulty swallowing: Pain or difficulty in swallowing can suggest problems in the throat or esophagus.
- Unexplained weight loss: Significant weight loss along with cough or hoarseness is concerning and should be assessed.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
If you or someone you know experiences a persistent cough or hoarseness lasting more than three weeks, especially if accompanied by other concerning symptoms (like weight loss, difficulty swallowing, or coughing up blood), it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider. Early evaluation and diagnosis can be crucial for effective treatment, especially in cases of cancer or other serious conditions.
7. Difficulty swallowing
Difficulty swallowing, known medically as dysphagia, can be a concerning symptom and may indicate various underlying health issues, including cancer. When it persists, especially in the absence of other apparent causes, it warrants medical attention. Here’s what you should know:
Potential Causes of Difficulty Swallowing:
Esophageal Cancer: One of the most common cancer-related causes of dysphagia is esophageal cancer. As the tumor grows, it can obstruct the esophagus, making it difficult to swallow food or liquids. This may also be accompanied by pain, weight loss, or regurgitation.
Throat Cancer: Cancers of the throat (pharynx) can lead to difficulty swallowing due to obstruction or inflammation, often accompanied by hoarseness, sore throat, or a lump in the neck.
Laryngeal Cancer: Similar to throat cancer, tumors in the larynx can interfere with swallowing and may also affect the voice.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): While not cancer, chronic GERD can cause inflammation and narrowing of the esophagus, leading to difficulty swallowing.
Neurological Disorders: Conditions like stroke, Parkinson’s disease, or multiple sclerosis can affect the nerves and muscles involved in swallowing.
Benign Tumors or Growths: Non-cancerous growths in the throat or esophagus can also cause swallowing difficulties.
Associated Symptoms to Monitor:
- Pain with swallowing: Known as odynophagia, this can occur alongside difficulty swallowing and may indicate inflammation or obstruction.
- Weight loss: Unintentional weight loss, particularly if you’re avoiding eating due to difficulty, is concerning.
- Choking or coughing while eating: Frequent choking or coughing during meals may signal a swallowing disorder.
- Regurgitation: The sensation of food coming back up into the throat can accompany swallowing difficulties.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
If you experience persistent difficulty swallowing that lasts more than a few weeks, especially if it’s accompanied by pain, weight loss, or changes in voice, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional.
An evaluation may include imaging studies, endoscopy, or other diagnostic tests to determine the underlying cause and guide appropriate treatment. Early detection is key, particularly when cancer or serious conditions are involved.
8. Unusual bleeding or bruising
Unusual bleeding or bruising can be significant warning signs and may indicate various health issues, including cancer. Here’s what to consider regarding these symptoms:
Types of Unusual Bleeding or Bruising:
Blood in Urine (Hematuria): The presence of blood in the urine may suggest cancers of the urinary tract, including bladder cancer or kidney cancer. It can also indicate infections or kidney stones.
Blood in Stool: This can signal colon cancer, rectal cancer, or other gastrointestinal conditions. Blood may appear bright red or dark, tarry, depending on where the bleeding originates.
Unexplained Vaginal Bleeding: Bleeding outside of a normal menstrual cycle, particularly after menopause, can indicate cancers of the reproductive system, such as uterine or cervical cancer.
Nosebleeds: Frequent or unexplained nosebleeds can sometimes be associated with blood disorders or cancers affecting the blood or bone marrow, like leukemia.
Easy or Unexplained Bruising: Bruising that occurs easily or without an obvious cause, especially if it’s frequent or severe, may indicate underlying blood disorders, including conditions related to leukemia or thrombocytopenia (low platelet count).
Gum Bleeding: Persistent bleeding from the gums while brushing teeth may suggest a blood disorder or leukemia.
Associated Symptoms to Monitor:
- Fatigue: If unusual bleeding or bruising is accompanied by extreme fatigue, it may suggest anemia or blood loss.
- Pale skin or shortness of breath: These can indicate significant blood loss and warrant immediate medical evaluation.
- Weight loss: Unexplained weight loss along with bleeding symptoms can indicate a more serious underlying condition.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
If you experience any form of unusual bleeding or bruising, especially if it persists, worsens, or is accompanied by other symptoms (such as fatigue, weight loss, or pain), it’s important to seek medical advice.
9. Changes in bowel habits
Changes in bowel habits can be important indicators of health issues, including potential cancers. It’s essential to pay attention to the nature of these changes, especially if they persist for more than a few weeks. Here are some key aspects to consider regarding changes in bowel habits:
Common Changes to Monitor:
Diarrhea: Persistent diarrhea, especially if it occurs frequently or is accompanied by other symptoms (such as weight loss or abdominal pain), can indicate colorectal cancer or other gastrointestinal issues.
Constipation: A significant change in bowel habits to constipation, especially if it is accompanied by abdominal discomfort or pain, can suggest potential blockages or tumors in the colon.
Narrowing of the Stool: Pencil-thin stools or changes in the shape of the stool can be a sign of colorectal cancer. This may indicate a narrowing of the bowel due to a tumor.
Blood in Stool: The presence of bright red or dark, tarry blood in the stool is a concerning sign and may indicate colon cancer, rectal cancer, or other gastrointestinal conditions.
Changes in Frequency: An increase or decrease in how often you have bowel movements, especially if it is significant and persistent, should be evaluated.
Mucus in Stool: The presence of excess mucus, especially if combined with other symptoms like diarrhea or blood, may indicate inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or colorectal cancer.
Associated Symptoms to Monitor:
- Abdominal pain or cramping: Ongoing discomfort in the abdomen, particularly if it accompanies bowel changes, can indicate underlying issues.
- Weight loss: Unintentional weight loss in conjunction with changes in bowel habits can be concerning and may suggest malignancy.
- Fatigue: Persistent fatigue may accompany changes in bowel habits, indicating anemia or other systemic issues.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
If you experience significant or persistent changes in bowel habits lasting more than a few weeks, especially if accompanied by other concerning symptoms (like blood in the stool, weight loss, or abdominal pain), it’s important to consult a healthcare provider.
10. Persistent bloating or abdominal pain
Persistent bloating or abdominal pain can be concerning symptoms and may indicate various health issues, including gastrointestinal disorders or cancers. It’s important to understand the context of these symptoms, especially if they last for an extended period or are accompanied by other signs. Here’s what to consider:
Potential Causes of Persistent Bloating or Abdominal Pain:
Ovarian Cancer: Bloating and abdominal discomfort are common symptoms of ovarian cancer. This may be accompanied by changes in appetite, weight loss, or urinary symptoms.
Gastrointestinal Cancers: Cancers of the stomach, pancreas, or colon can cause persistent bloating and abdominal pain. Symptoms may include changes in bowel habits, unexplained weight loss, or blood in the stool.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): While not cancer, IBS can cause chronic bloating and abdominal pain. Symptoms may fluctuate between constipation and diarrhea.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Conditions like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis can lead to persistent abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and weight loss.
Gallbladder Disease: Conditions affecting the gallbladder, such as gallstones or inflammation, can cause abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right abdomen, often accompanied by bloating.
Celiac Disease: This autoimmune disorder can lead to bloating and abdominal pain due to an adverse reaction to gluten.
Associated Symptoms to Monitor:
- Changes in bowel habits: Diarrhea or constipation alongside bloating and pain can indicate serious gastrointestinal issues.
- Weight loss: Unexplained weight loss in conjunction with abdominal symptoms is particularly concerning.
- Nausea or vomiting: Persistent nausea or vomiting may indicate obstruction or other serious conditions.
- Fatigue: General fatigue can signal underlying health issues, including cancer.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
If you experience persistent bloating or abdominal pain lasting more than a few weeks, especially if accompanied by other symptoms (such as weight loss, changes in bowel habits, or nausea), it’s important to consult a healthcare provider.
They can perform diagnostic tests (like imaging studies or endoscopy) to determine the underlying cause and guide appropriate treatment. Early detection is crucial, particularly for conditions like ovarian or gastrointestinal cancers.
Conclusion
What are 20 warning signs of cancer? We feel this article is very important to determine the underlying cause and guide the appropriate treatment. Because the few warnings or signs mentioned here are very important. Hope you can understand. Visit regularly to see more such articles.





